About Photocatalyst
- Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations.
- Photocatalyst is the acceleration of a photoreaction in the presence of a catalyst. In catalyzed photolysis, light is absorbed by an adsorbed substrate.
- We usually using photocatalyst is Titanium dioxide. It is chemically stable substance.
- Titanium dioxide (chemical formula: TiO2) may take on any of the three crystal structures. One of them is rutile, which tends to use for a white pigment that surface covered type, beauty product and so on. Other of them is anatase, which tends to use for a photocatalyst coating materials. Another of them is brookite, which is only artifactually-produced crystal substance. It has photocatalysis effect, but it does not general use for photocatalyst coating fluid.
- Our M-Clean series are used an anatase type and brookite type of crystal substance. The titanium dioxide of the anatase type and the brookite type generally show a higher photoactivity than the rutile type.
Decomposed effect
- Photocatalyst M-Clean has a feature of two photocatalysis properties. One of them is high decompose effect. This decompose effect is able to remove stains from several surface. Following photograph is decomposed organic substance (blue ink) condition.
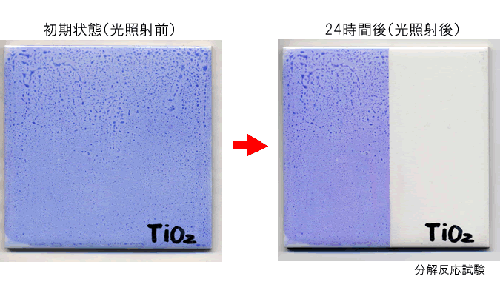
Photograph of photocatalysis decompose effect
(Decomposed blue ink by photocatalysis effect)
What happens when titanium dioxide is exposed to light?
- Photocatalyst M-Clean can decompose several organic substances that are several odor gas, formaldehyde and other chemical substances, bacterial, mold and so on.
- It can be used several situation, regardless of the exterior or room and it bring out great performance, such as self-cleaning on a wall, air purification effect, anti bacterial effect and anti mold effect.
- M-Clean has a lot of promise to improve the environment.
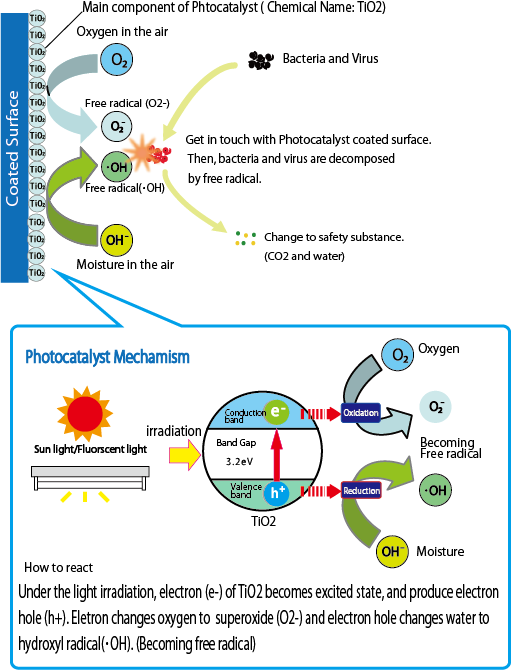
- The photocatalyst reaction principle is following process.
Process of photocatalysis reaction
Super hydrophilic property
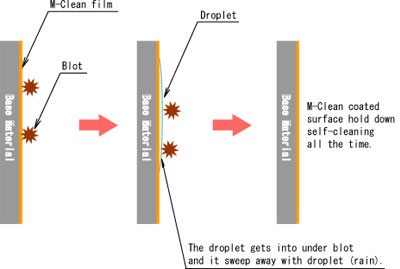
- Another of them is super hydrophilic property. This property is that rain gets into under some blot or oil, then rainwater striked up them. After that blot or oil is sweep away with rain water.
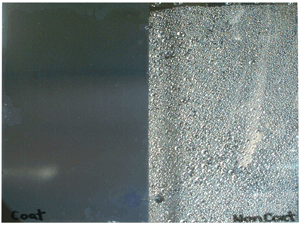
Photograph of super hydrophilic condition
(Left side: Hydrophilic condition with photocatalysis effect)
- "Hydrophilicity" means to get wet easily on surface condition. Such as made waterdrop on something surface after rain that water shedding condition. The hydrophilic property is spread water and looks like water film on the surface.
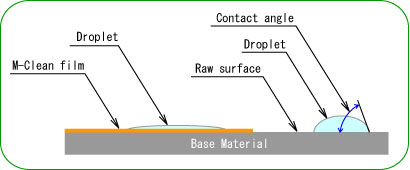
- The droplet is spread on photocatalyst coating surface because TiO2 is activated by light irradiation and the water contact angle becomes almost 0 level. Various material surface conditions can be changed to hydrophilicity by this photocatalyst performance.
- Some blot put on the M-Clean coated surface that is able to flush away together with water (such as rain) on super hydrophilic surface.
- This effect is used flush away on a surface of building external wall, cool down building wall at summer season, etc.
By using the hydrophilic effect of photocatalyst, it is found to be useful for cost reduction for maintenance, improvement of electricity expense, landscape management, environmental protection, etc.
High transparency
- M-Clean is able to apply on glass, window and several transparency plastics. Uaual photocatalyst coating fluid cannot apply on these materials, because of become clouded by photocatalyst. M-Clean can be used for several transparency materials and lustrous materials

M-Clean coated condition
(Applied M-Clean on the glass of right side from center)
More mechanism information is from here
